What Is Magnetic Levitation and How Does It Work

Magnetic levitation lets you see objects float in the air without touching anything. You watch as strong magnetic fields push or pull, holding things above the ground. This process does not need wires or strings. You find it in science experiments and some fast trains. Magnetic levitation uses invisible forces to lift objects and keep them steady.
キーテイクアウト
Magnetic levitation allows objects to float without contact, using strong magnetic fields to lift and stabilize them. This technology is seen in maglev trains and science experiments.
Two main methods of magnetic levitation are Electro-Magnetic Suspension (EMS) and Electro-Dynamic Suspension (EDS). Both methods reduce friction, enabling high-speed travel.
Superconducting magnets play a crucial role in magnetic levitation. They require very low temperatures to function, allowing for frictionless movement and energy efficiency.
Maglev trains offer faster and smoother rides compared to traditional trains. They consume less energy and produce fewer emissions, making them a cleaner transportation option.
You can explore magnetic levitation at home with simple experiments using magnets. This hands-on approach helps you understand the principles of magnetic forces and levitation.
What Is Magnetic Levitation
Simple Definition
You see magnetic levitation when an object floats above another without touching it. This happens because strong magnetic fields push or pull the object, keeping it in the air. You do not need wires, strings, or any physical support. Magnetic levitation uses magnets to create invisible forces that lift and hold things up. You find this technology in maglev trains, science demonstrations, and some toys.
ヒント: Magnetic levitation is different from other types of levitation.
Magnetic levitation uses magnetic fields to suspend objects.
Electrostatic levitation uses electric fields to lift charged objects, like in the famous oil drop experiment.
Aerodynamic levitation uses air or gas to keep objects floating, such as a ping pong ball held up by a stream of air.
Basic Principle
You can understand magnetic levitation by looking at how magnets interact. When you place two magnets with the same poles facing each other, they push away. This force can lift one magnet above the other. You also see magnetic levitation in superconductors. When you cool a superconductor, it expels magnetic fields and floats above a magnet. This effect is called the Meissner effect.
The science behind magnetic levitation relies on several physical laws:
Faraday’s Law explains how changing magnetic fields create electric currents.
Lenz’s Law shows that these currents make magnetic fields that push against the original field, causing repulsion.
The Meissner effect lets superconductors repel magnetic fields and float.
You see these principles in action with maglev trains. The train floats above the tracks, reducing friction and allowing high speeds. You can also try simple experiments at home, like floating a magnet above another or watching a superconductor levitate.
How Magnetic Levitation Works

Magnetic Repulsion
You can see magnetic repulsion in action when you place two magnets with the same poles facing each other. They push away, and this force can lift one magnet above the other. In maglev trains, engineers use this principle to make the train float above the tracks. You find two main methods for levitation: Electro-Magnetic Suspension (EMS) and Electro-Dynamic Suspension (EDS).
EMS uses electromagnets to attract the train toward an iron rail, lifting it slightly.
EDS uses superconducting magnets to create strong repulsive forces, lifting the train several centimeters above the guideway.
の propulsion system uses alternating current to create magnetic fields. These fields use both attraction and repulsion to move the train forward.
Magnets on the train and the track work together. Some pull the train from the front, while others push it from behind.
Magnetic repulsion removes friction from wheels, allowing the train to travel at high speeds. You can try simple experiments at home by stacking ring magnets and watching them float apart. Students often build prototypes to test how repulsion can lift objects, learning about magnetic levitation through hands-on activities.
Superconducting Magnets
Superconducting magnets play a big role in magnetic levitation. You need to cool a superconductor to very low temperatures, around -163°C (-261°F). When you place a powerful magnet near the superconductor, the Meissner effect starts. This effect pushes the magnetic field out and causes the superconductor to float.
You cool the superconductor to the right temperature.
You bring a strong magnet close to the superconductor.
If conditions are right, flux pinning happens. The superconductor locks the magnetic field lines and stays in place.
Superconducting magnets help maglev trains move smoothly and efficiently. They allow frictionless and contactless motion, which means less energy is lost. Recent improvements have made these systems more stable and reduced vibrations. You see flux pinning in classroom demonstrations, where a superconductor hovers above a magnet and stays steady even if you tilt it.
Induced Magnetic Fields
Induced magnetic fields also help with magnetic levitation. When you change the magnetic field near a conductor, you create electric currents. These currents make their own magnetic fields, which can push against the original field. This process is important for maglev trains and other levitation systems.
The reconnection electromagnetic launch system uses pulse capacitors to supply energy. Some of the electrical energy turns into mechanical energy, making the armature move faster. Another part becomes magnetic energy, increasing the magnetic field around the driving coil.
Maglev trains use magnetic fields to suspend, guide, and propel the vehicle along the track. This technology provides a cleaner and more sustainable solution for transportation. You see less energy usage and fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to regular trains.
You can watch spinning disc experiments in science labs to see induced magnetic fields at work. These setups use electromagnetic bases or adjustable ring magnets to keep a disc floating for several minutes. Large-scale demonstrations help scientists measure how levitation forces and stability change. DIY versions use neodymium magnets and 3D-printed parts, making magnetic levitation easy to explore at home or in school.
説明 | 重要な機能 | |
|---|---|---|
Electromagnetic Base | Applies periodic forcing to counteract air drag | Enhances levitation time beyond two minutes |
Adjustable Ring Magnet Base | Fine-tunes spacing for optimal levitation height | Allows precise control without active feedback |
Large-scale Demonstrations | Facilitates precision measurements of dynamic behavior | Studies levitation forces and stability at larger scales |
DIY Versions | Utilizes neodymium magnets and 3D-printed components | Highlights accessibility for educational purposes |
You see magnetic levitation in many experiments and real-world applications. These principles help engineers design faster, safer, and more efficient transportation systems.
Key Components and Technologies
Types of Magnets
You find several types of magnets in magnetic levitation systems. Each type has unique strengths and uses.
Permanent magnets
Electromagnets
Superconducting magnets
Ferromagnetic materials
Diamagnetic materials
Induced current magnets
Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) 磁石
Neodymium magnets give you strong magnetic properties. You see them in electronics, wind turbines, and electric vehicle motors. Superconducting magnets create very strong fields when cooled to low temperatures. These magnets help trains float and move smoothly.
Type of Magnet | Field Strength |
|---|---|
Superconducting electromagnets | 1.5 T – 3 T (clinical) to 7 T+ (research) |
Magnetic Levitation Magnets | Varies widely; often lower for everyday applications |
You use different magnets depending on the application. Everyday products need less strength. High-speed trains need powerful magnets for safe and stable levitation.
Guideways and Control Systems
Guideways give you a path for the train or object to follow. Engineers design these tracks to work with the magnets. The guideway must stay smooth and strong to support high speeds. Control systems help manage the forces that keep the train floating and centered.
Evidence Description | Implication for Stability |
|---|---|
Simulation models include aerodynamic loads for high-speed maglev trains. | You can analyze how wind affects stability. |
Crosswinds can interact with the train and guideway. | You need to understand these effects to prevent derailment. |
Feedback control systems manage levitation and guidance. | Good control systems keep the train stable during operation. |
You see sensors and computers working together. They adjust the magnetic forces in real time. This keeps the train safe, even when wind or other forces try to push it off track.
Stability and Safety
You want magnetic levitation systems to stay safe and steady. Engineers use feedback control to adjust the magnetic fields quickly. This helps the train stay balanced, even at high speeds or in strong winds. You also see safety features built into the guideways and vehicles.
Maglev trains need less maintenance than regular trains. The train does not touch the track, so there is less wear and tear. This means lower costs and fewer repairs. You get a reliable and sustainable transportation system.
ヒント: The lack of friction in magnetic levitation systems means less noise and smoother rides for passengers.
Magnetic Levitation Applications
Maglev Trains
You see maglev trains as one of the most exciting uses of magnetic levitation. これらの列車は線路の上に浮かんでいます, moving without wheels. You experience smoother rides and faster travel. Maglev trains use strong magnets to lift and guide the train. You find them in cities like Shanghai and Tokyo. The table below shows two popular maglev train models and their speeds:
Maglev Train Model | Operational Speed (km/h) | Operational Speed (時速マイル) |
|---|---|---|
431 | 268 | |
L0 Series SCMaglev | 603 | 375 |
You notice that maglev trains travel much faster than regular trains. They use less energy at high speeds because they do not have rolling resistance or friction from wheels. The table below compares maglev trains to traditional rail systems:
特徴 | Maglev Trains | Traditional Rail Systems |
|---|---|---|
Rolling Resistance | None | Present |
Friction | Significantly reduced | 高い |
Lower per mile traveled | Higher per mile traveled | |
Speed Potential | Very high | Limited |
Industrial Uses
You find magnetic levitation in factories and clean rooms. Manufacturers use maglev conveyor systems to move parts without friction. This reduces wear and tear, saving money on repairs. You see wafer stages in chip factories using magnetic levitation to avoid contact, which keeps the environment clean and safe for sensitive electronics. Here are some benefits:
Zero mechanical friction means less maintenance and longer equipment life.
Ultra-clean operation keeps dust and particles away from delicate chips.
Precision movement improves accuracy in chip making.
Reduced vibration helps with nanometer-scale tasks.
You also see maglev systems in industries like pharmaceuticals and food production, where hygiene is very important.
Everyday Products
You use magnetic levitation in some toys, gadgets, and science kits. Floating globes and spinning displays use magnets to create eye-catching effects. You find maglev technology in some speakers and motors, making them quieter and more efficient. Researchers have developed levitating disks for sensitive measurements in physics labs. New magnet designs improve medical imaging and other devices.
🚀 In the future, you may ride maglev trains in more cities, see faster cargo transport, and even watch space launches using magnetic levitation. Experts believe this technology will make urban transportation cleaner, 静かになる, and more efficient.
You have learned that magnetic levitation uses EMS and EDS to lift objects without contact. You see maglev trains, medical devices, and clean industrial machines using this technology. 磁気浮上 reduces energy use and pollution, as shown in the chart below.
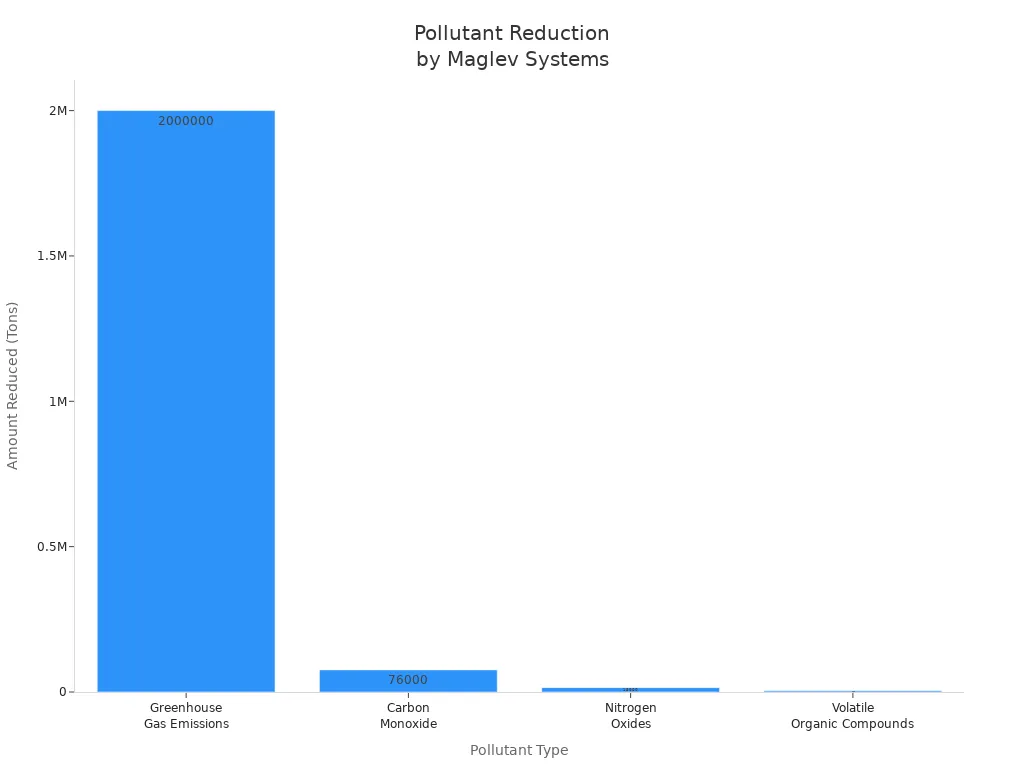
You can build simple maglev projects in school and explore new ideas. High costs and limited adoption remain challenges, but you may see more magnetic levitation in future cities and industries.
よくある質問
What is the main benefit of magnetic levitation?
You get smoother and faster movement. Magnetic levitation removes friction, so trains and machines run quietly and efficiently. You also see less wear and tear, which means lower maintenance costs.
Can you build a simple magnetic levitation project at home?
You can build a basic maglev project using ring magnets and a pencil. Stack the magnets with like poles facing each other. Watch the top magnet float. This experiment helps you learn about magnetic repulsion.
Are maglev trains safe for passengers?
You ride safely on maglev trains. Engineers use strong control systems and sensors to keep the train stable. You experience fewer accidents because the train does not touch the track.
Where do you see magnetic levitation outside of trains?
You find magnetic levitation in toys, speakers, and science kits. Factories use maglev systems to move parts without friction. Hospitals use magnetic levitation in some medical devices for cleaner and quieter operation.
How does magnetic levitation help the environment?
You help the environment by using maglev technology. Maglev trains use less energy and produce fewer greenhouse gases. You see cleaner air and quieter cities when more people use magnetic levitation systems.


